Demographics of Italy

Italy has the fifth-highest population density in Europe — about 196 persons per square kilometer (490 per square mile). From being a country of mass-emigration, in the last twenty years, Italy has become quite a large immigrant-receiving country, with over 7.5% of the nation's population being from abroad.[1] Even though Italy's population is climbing, it is exclusively to the influx of migrations. The nation has a relatively low fertility rate,[2] of 1.41 children per family, while having the world's 19th highest life expectancy, coming after New Zealand and Bermuda, and beating Gibraltar and Monaco.[3]
Population
At the start of 2009, the total resident population was 60,045,068 [4]. Italy currently has the fourth largest population in the European Union, and the 23rd largest population in the world. Italy's population density at 196.1 persons per kilometre is the fifth highest in the European Union. The highest density is in Northern Italy, as one third of the country contains almost half of the Italian population. After World War II, Italy saw an economic boom which led to rural population moving to the cities, and in the same time it turned from a nation characterized by massive emigration to a net immigrant-receiving country. High fertility persisted until the 1970s when it plunged below replacement so as of 2007, one in five Italians was pensioners. Despite this, thanks mainly to the immigration of 1980s and 1990s, in 2000s Italy saw natural population growth for the first time in years.[5]
Families: 23,907,410 (58,802,902 Italians in a familiar status, 2.5 Italians per family)
- Most populous comune (residents) Rome
- Least populous comune (residents) Morterone (LC) 33
- Greatest human density (residents per km²) Portici (NA) 13,032.1
- Greatest comune territory (km²) Rome (RM) 1,285.30
- Smallest comune territory (km²) Fiera di Primiero (TN) 0.15
Metropolitan areas
According to the OECD,[6] the largest metropolitan areas are:
| N° | Municipality | Metropolitan City | Metropolitan Area | Superf. (in km²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rome | 3.800.000 | 4.340.000 | 3.089 km2 |
| 2 | Milan | 3.000.000 | 7.000.000 | 12.000 km2 |
| 3 | Naples | 2.200.000 | 5.000.000 | 2.300 km2 |
| 4 | Turin | 1.460.000 | 1.700.000 | 1.127 km2 |
| 5 | Palermo | 860.000 | 1.040.000 | 1.391 km2 |
| 6 | Genoa | 745.000 | 1.400.000 | 4.200 km2 |
| 7 | Bari | 620.000 | 1.000.000 | 2.270 km2 |
| 8 | Florence | 600.000 | 1.500.000 | 4.844 km2 |
| 9 | Bologna | 580.000 | 980.000 | 3.703 km2 |
| 10 | Catania | 580.000 | 760.000 | 939 km2 |
| 11 | Cagliari | 370.000 | 470.000 | 1.800 km2 |
| 12 | Venice | 360.000 | 3.270.000 | 6.680 km2 |
| 13 | Messina | 250.000 | 480.000 | 1.135 km2 |
| 14 | Reggio Calabria | 240.000 | 380.000 | 1.165 km2 |
| 15 | Trieste | 220.000 | 240.000 | 212 km2 |
Cities ranked by population
Population figures within the limits of the city proper, from the December 2004 Istat report (www.istat.it):
Main cities of Italy
A brief description of Italy's main cities:




.jpg)
- Rome (English pronunciation: /ˈroʊm/; Italian: Roma [ˈroːma]; Latin: Roma) is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populous municipality (central area), with over 2.7 million residents in 1,285.3 km2 (496.3 sq mi), while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat to be 3.46 million.[7] The metropolitan area of Rome is estimated by OECD to have a population of 3.7 million.[8] It is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber river. Rome's history as a city spans over two and a half thousand years, as one of the founding and most powerful cities of Western Civilisation. It was the centre of the Roman Empire, which dominated Europe, North Africa and the Middle East for over four hundred years from the 1st Century BC until the 4th Century AD, and during the Ancient Roman era, the city was the most powerful in Europe.[9] Besides being Italy's administrative capital, Rome is a major European centre for politics, religion, culture and finance, home of worldwide organizations such as FAO.[10] The city itself is Italy's richest by purchasing power, with a GDP of €94.376 billion ($121.5 billion),[11] and is the world's 18th most expensive city (in 2009).[12] Home of the Vatican City, where the pope, the head of the Roman Catholic Church, resides, Rome is a global centre for pilgrimage, and is one of the world's most visited cities,[13] containing numerous priceless works of art, archaeological sites, palaces, museums, churches, parks and villas.
- Milan (Italian: Milano Italian pronunciation: [miˈla(ː)no]; Lombard: Milan (listen)), is the capital of the region of Lombardia and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while the urban area is the fifth largest in the E.U. with an estimated population of 4.3 million.[14] The Milan metropolitan area, by far the largest in Italy, is estimated by OECD to have a population of 7.4 million.[15] Milan is, along with Rome, Italy's capital of business, design, finance, media and industry. The city proper is Italy's second richest, with a GDP of $115 billion, whilst the metropolitan area has Europe's 4th highest GDP, that of € 241.2 billion (US$ 312.3 billion) in 2004, which means that were Milan a country, it would be the world's 28th richest, near in size to that of the economy of Austria. Milan is also a major international fashion capital, annually competing with other centres such as Paris, New York City, London, Los Angeles and Tokyo.[16] The city also hosted the World Exposition in 1906 and will host the Universal Expo in 2015, and currently the FieraMilano fair is considered the largest in Europe.
- Naples (Italian: Napoli [ˈnaːpoli], Neapolitan: Napule) is the capital of the region of Campania and of the province of Naples. The city proper has a population of around 1 million people, while the population of urban area is estimated by Eurostat to be 2.25 million. The Naples metropolitan area, according to different sources, is the second after the Milan metropolitan area (with 4.434.136 inhabitants according to SVIMEZ DATA[17] or 4.996.084 according to CENSIS INSTITUTE[18]) or the third (3.1 million inhabitants according to OECD[19]) most populous metropolitan area in Italy.Naples is ranked fourth in Italy, for economic strength, after Rome, Milan and Turin. Naples is a thriving and cosmopolitan metropolis with a GDP of $43 billion.[20] Naples is one of the oldest cities of the western world, whose current urban structure retains elements of its long and eventful history. Founded by the Ancient Greeks as "Νεάπολις", Neápolis (New City), it held an important role in Magna Graecia and then as part of the Roman Republic in the central province of the Empire. The city has seen a multitude of civilizations come and go, each leaving their mark and now the historic city centre is listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. Naples was the capital city of a kingdom which bore its name from 1282 until 1816 in the form of the Kingdom of Naples, then in union with Sicily it was the capital of the Two Sicilies until the Italian unification. Naples has profoundly influenced many areas of Europe and beyond.[21]
- Turin (Italian: Torino pronounced [toˈriːno]; Piedmontese: Turin; pronounced [tyˈɾiŋ]) is a major city as well as a business and cultural centre in northern Italy, capital of the Piedmont region, located mainly on the left bank of the Po River surrounded by the Alpine arch. The population of the city proper is 909,193 (November 2008) while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat to be 1.7 million inhabitants; the Turin metropolitan area is estimated by OECD to have a population of 2.2 million.[8] Turin is well known as the home of the Shroud of Turin, the football teams Juventus F.C. and Torino F.C., the headquarters of automobile manufacturers Fiat, Lancia and Alfa Romeo, and as host of the 2006 Winter Olympics. Several International Space Station modules, such as Harmony and Columbus, were also manufactured in the city. It was the capital of the Duchy of Savoy from 1563, then of the Kingdom of Sardinia ruled by the Royal House of Savoy and finally the first capital of a unified Italy.[22] Turin ranks third, after Rome and Milan, for economic strength,[23] with a GDP of $58 billion. It is often referred to as "the Capital of the Alps". Turin is also known as "the Automobile Capital of Italy" or the Detroit of Italy; in Italy it is also called "[La] capitale Sabauda".
- Palermo ([paˈlɛrmo], Sicilian: Palermu, Latin: Panormus, from Greek: Πάνορμος, Panormos) is a historic city in Southern Italy, the capital of the autonomous region Sicily and the Province of Palermo. The population of the Palermo urban area is estimated by Eurostat to be 855,285, while its metropolitan area is the fifth most populous in Italy with around 1.2 million people. In the central area, the city itself has a population of around 670 thousand people, the inhabitants are known as Palermitans or poetically panormiti, the languages spoken by its inhabitants are the Italian language and the Sicilian language. The city is noted for its rich history, culture, architecture and gastronomy, playing an important role throughout much of its existence; it is over 2,700 years old. Palermo is located in the northwest of the island of Sicily, right by the Gulf of Palermo in the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is Sicily's cultural, economic and touristic capital, and Palermo's main industrial sectors include tourism, services, commerce and agriculture.[24]
Immigration
Traditionally a country of emigrants, in the last 20 years Italy has become a country of immigration, with about 7.5% of the population fitting that description. 156,179 foreigners were counted in the 1971 census, (Source: Italian Caritas); according to the last figure (Caritas est. 2009[25]), 5 million immigrants live legally in Italy, while estimates for undocumented immigrants vary from 0.8 million to 2 million.
Officially, at the end of 2008, foreigners comprised 7.5% of the population or 4,800 000 persons,[26] an increase of 470,000 since the previous year. In some Italian cities, such as Brescia, Milan, Padua, and Prato, immigrants total more than 15% of the population.
Italy now has an estimated 4 million to 5 million immigrants — about 7 percent of the population. Since the expansion of the European Union, the most recent wave of migration has been from surrounding European nations, particularly Eastern Europe, and increasingly Asia, replacing North Africa as the major immigration area. Some 900,000 Romanians are officially registered as living in Italy, replacing Albanians and Moroccans as the largest ethnic minority group, but independent estimates put the actual number of Romanians at double that figure or perhaps even more. Others immigrants from Eastern Europe are Ukrainians ( 200 000 ), Polish ( 100 000 ),Moldovans ( 90 000 ) Macedonians ( 81 000 ), Serbs ( 75 000 ), Bulgarians ( 54 000 ), Bosnians ( 40 000 ), Russians ( 39 600 ), Croatians ( 25 000 ), Slovakians ( 9000 ), Hungarians ( 8600 ). ( [37] As of 2009, the foreign born population origin of Italy was subdivided as follows: Europe (53.5%), Africa (22.3%), Asia (15.8%), the Americas (8.1%) and Oceania (0.06%). The disribution of foreign born population is largely uneven in Italy: 87.3% of immigrants live in the northern and central parts of the country (the most economically developed areas), while only 12.8% live in the southern half of the peninsula.

Many illegal immigrants from Africa and Eastern Europe work as day laborers in the agriculture of Southern Italy, especially in the citrus and olive groves of Calabria and the tomato factories of Puglia. African immigrants typically pay smugglers in Libya for a transit to the Italian island of Lampedusa. From there they are transferred to detention camps in mainland Italy.
Foreign residents by country of citizenship in 2008
| Group | % |
|---|---|
| Romania | 23.2% |
| Albania | 12.9% |
| Morocco | 11.8% |
| People's Republic of China | 5.0% |
| Ukraine | 4.5% |
| Philippines | 3.3% |
| Tunisia | 2.9% |
| Poland | 2.9% |
| India | 2.7% |
| Moldova | 2.6% |
Source: ISTAT - Istituto Nazionale di Statistica[27]
Foreign residents by region in 2008
| Region | % |
|---|---|
| Emilia-Romagna | 8.5% |
| Umbria | 8.5% |
| Lombardy | 8.4% |
| Veneto | 8.3% |
| Marche | 7.4% |
| Tuscany | 7.4% |
| Lazio | 7.0% |
| Piedmont | 7.0% |
| Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol | 6.9% |
| Friuli-Venezia Giulia | 6.7% |
| Liguria | 5.8% |
| Aosta Valley | 5.2% |
| Abruzzo | 4.5% |
| Calabria | 2.5% |
| Molise | 2.0% |
| Campania | 2.0% |
| Apulia | 1.9% |
| Sicily | 1.9% |
| Basilicata | 1.6% |
| Sardinia | 1.5% |
Source: ISTAT - Istituto Nazionale di Statistica[28]
Languages
The official and common language is Italian. Official recognized minority language groups are:
| Group | Population | Native language | Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lombard | 6,375,000 | Lombard | Lombardy |
| Piedmontese | 3,957,000 | Piedmontese | Piedmont |
| Venetian | 3,872,000 | Venetian | Veneto |
| Emilian | 2,968,000 | Emilian | Emilia |
| Romagnolo | 1,648,000 | Romagnolo | Romagna |
| Ligurian | 875,000 | Ligurian | Liguria |
| Sardinian | 1,269,000 | Sardinian | Sardinia |
| Friulian | 526,000 | Friulian | Friuli-Venezia Giulia |
| Albanian | 348,813[29] | Albanian | southern Italy, Sicily |
| Tyrolean | 290,000 | German | Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol |
| Occitan | 178,000 | Occitan | Piedmont, Liguria, Calabria |
| Roma/Sinti | 130,000 | Estrekárja (German), Valshtiké (French), Piemontákeri (Piedmont) | North, North-West |
| Roma | 130,000 | Romany | the whole country |
| Sard.Sassarese | 125,000 | Sassarese | North-west Sardinia |
| Corsican | 100,000 | Gallurese | North-east Sardinia |
| Franco-Provençal | 90,000 | Franco-Provençal | Piedmont, Aosta Valley, Apulia |
| Slovene | 80,000 | Slovene | Friuli-Venezia Giulia |
| Ladin | 55,000 | Ladin | Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, Veneto |
| French | 20,000 | French | Aosta Valley |
| Greek | 20,000 | Griko (Greek) | Calabria, Apulia |
| Catalan | 18,000 | Alguerese (Catalan) | Sardinia |
| Croatian | 2,600 | Croatian | Molise |
| Carinthian | 2,000 | German | Friuli-Venezia Giulia |
| Carnian | 1,400 | Friulian | Friuli-Venezia Giulia |
Source: Ministero degli Interni del Governo Italiano.
Official status:
- German is co-official in the province of Bolzano-Bozen, where in 1991 there were 287,503 German and 116,914 Italian speaking people.
- Standard French is co-official in the Aosta Valley, but the spoken dialects of this region, and of some northern valleys of Piedmont, are more precisely Franco-Provençal, which boasts some differences from standard French.
Religion
Roman Catholicism is by far the largest religion in the country, although the Catholic Church is no longer officially the state religion. 87.8% of Italians identified as Roman Catholic,[30] although only about one-third of these described themselves as active members (36.8%). Other Christian groups in Italy include more than 700,000 Eastern Orthodox Christians,[31] including 470,000 newcomers[32] and some 180,000 Greek Orthodox, 550,000 Pentecostals and Evangelicals (0.8%), of whom 400,000 are members of the Assemblies of God, 235,685 Jehovah's Witnesses (0.4%),[33] 30,000 Waldensians,[34] 25,000 Seventh-day Adventists, 22,000 Mormons, 15,000 Baptists (plus some 5,000 Free Baptists), 7,000 Lutherans, 5,000 Methodists (affiliated to the Waldensian Church).[35] The country's oldest religious minority is the Jewish community, comprising roughly 45,000 people (0.06%). It is no longer the largest non-Christian group. As a result of significant immigration from other parts of the world, some 1,000,000 Muslims[36] (1.8% of the total population) live in Italy, though only 50,000 are Italian citizens. In addition, there are 110,000 Buddhists (0.2%),[32][37][38] 70,000 Sikhs,[39] and 70,000 Hindus (0.1%) in Italy.
Demographic statistics from the CIA World Factbook
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.
Population estimate
- 60,724,922 (Neodemos, May 2010)
Age structure
- 0-14 years: 14.03% (male 4,302,487; female 4,064,556) (2008)
- 15-64 years: 65.93% (male 19,647,451; female 19,658,810) (2008)
- 65 years and over: 20.04% (male 4,999,809; female 6,946,177) (2008)[4]
- 0-14 years: 13.5% (male 4,056,156/female 3,814,070)
- 15-64 years: 66.3% (male 19,530,696/female 18,981,084)
- 65 years and over: 20.2% (male 4,903,762/female 6,840,444) (2009 est.)
Population growth rate
- +0.721% (2008)
Birth rate
- 9.6 births/1,000 population (2009 est.)
Death rate
- 9.70 deaths/1,000 population (2008)
Gender ratio
- at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
- under 15 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
- 15-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.72 male(s)/female
- total population: 0.96 male(s)/female
(2004 est.)
Infant mortality rate
- total: 5.51 deaths/1,000 live births
- male: 6.07 deaths/1,000 live births
- female: 4.91 deaths/1,000 live births
(2009 est.)
Total fertility rate
- 1.45 children born/woman (2009 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
- total population: 80.2 years (2009 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate
- 0.5% (2001 est.)
- 0.4% (2009 est.)
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS
- 140,000 (2001 est.)
- 150,000 (2007 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths
- less than 1,000 (2003 est.)
- 1,900 (2007 est.)
Nationality
- noun: Italian(s)
- adjective: Italian
Ethnic groups
Italian: 92.5%, other European (mostly Albanian, Romanian, Ukrainian and others) 4%, North African (mostly Berber) 2%, others 1.5%[40]
Religious groups
Roman Catholic:90% (approximately; one third practicing), other Christians: 2%, Muslim: 3%, Atheist or Agnostic: %
Literacy
- definition: age 15 and over can read and write
- total population:
- male: 99%
- female: 98.3%
(2003 est.)
Genetic
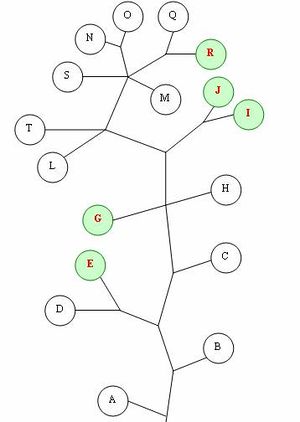
In a very recent and thorough study (2007) which analysed 699 Italian individuals from 12 different regions in continental Italy,[41] the most common Y-dna haplogroups observed were :
- R1 (42.8% : 40% R1b and 2.8% R1a)
- J (22 % : 20% J2 and 2% J1)
- E1b1b (12.6 %)
- G (10.8 %)
- I (7.5 %)
- K (3.7%)
See also
- List of Italians
- Italian diaspora
References
- ↑ http://demo.istat.it/str2009/index.html
- ↑ http://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/wpp2006/WPP2006_Highlights_rev.pdf
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2102rank.html
- ↑ Statistiche demografiche ISTAT:
- ↑ Statistiche demografiche ISTAT:
- ↑ OECD. "Competitive Cities in the Global Economy" (PDF). http://213.253.134.43/oecd/pdfs/browseit/0406041E.PDF. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ↑ "Urban Audit". Urbanaudit.org. http://www.urbanaudit.org/DataAccessed.aspx. Retrieved 2009-03-03.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 OECD. "Competitive Cities in the Global Economy". http://213.253.134.43/oecd/pdfs/browseit/0406041E.PDF. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ↑ "Rome And Its Power. Part Iii Of The Premier Web Site On Western Civilization". Omnibusol.com. http://www.omnibusol.com/anrome.html. Retrieved 2009-10-17.
- ↑ "Working opportunities with FAO". Fao.org. http://www.fao.org/VA/Employ.htm. Retrieved 2009-10-17.
- ↑ "World's richest cities by purchasing power". City Mayors. http://www.citymayors.com/economics/usb-purchasing-power.html. Retrieved 2009-10-17.
- ↑ "Cost of living - The world's most expensive cities 2009". City Mayors. 2009-07-07. http://www.citymayors.com/features/cost_survey.html. Retrieved 2009-10-17.
- ↑ Caroline Bremner. "Top 150 City Destinations London Leads the Way". Euromonitor International. http://www.euromonitor.com/Top_150_City_Destinations_London_Leads_the_Way. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ Demographia: World Urban Areas
- ↑ OECD. "Competitive Cities in the Global Economy" (PDF). http://213.253.134.43/oecd/pdfs/browseit/0406041E.PDF. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ↑ The Global Language Monitor » Fashion
- ↑ "Seminario-aprile2001.PDF" (PDF). http://users.libero.it/domenico.smarrazzo/studio.PDF. Retrieved 2009-07-19.
- ↑ http://www.censis.it/files/Rapporto_annuale/2008/2_societa_italiana_2008.pdf
- ↑ OECD. "Competitive Cities in the Global Economy" (PDF). http://213.253.134.43/oecd/pdfs/browseit/0406041E.PDF. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ↑ City Mayors reviews the richest cities in the world in 2005
- ↑ Centro Storico di Napoli
- ↑ "The city's history". Turismo e promozione. Città di Torino. http://www.comune.torino.it/canaleturismo/en/history.htm. Retrieved 2007-08-31.
- ↑ CENSIS
- ↑ The Times | Business City Guide
- ↑ http://www.caritasroma.it/Prima%20pagina/Download/Dossier2009/scheda%20di%20sintesi%202009.pdf
- ↑ Statistiche demografiche ISTAT
- ↑ http://demo.istat.it/str2008/index.html
- ↑ http://demo.istat.it/strasa2009/index.html
- ↑ istat.it - see page 6
- ↑ Italia, quasi il 79% si proclama cattolico
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 [2]PDF (65.4 KB)
- ↑ Le religioni in Italia: I Testimoni di Geova:
- ↑ Chiesa Evangelica Valdese - Unione delle chiese Metodiste e Valdesi:
- ↑ [3]
- ↑ BBC NEWS | Europe | Muslims in Europe: Country guide:
- ↑ Unione Buddhista Italiana: l'Ente
- ↑ SGI-ITALIA.ORG: L'Istituto Buddista Italiano Soka Gakkai:
- ↑ Etnomedia
- ↑ Statistiche demografiche ISTAT
- ↑ Y chromosome genetic variation in the Italian peninsula is clinal and supports an admixture model for the Mesolithic-Neolithic encounter, Capelli et al. 2007
External links
- Demographic page (English)
- Demographic Profile Italy Allianz Knowledge
|
||||||||||||||